XACT¶
Note
eXtended Anatomically Constrained Tractography (XACT) is currently an experimental feature in Trekker.
Please submit an issue in our GitHub repository or send an e-mail to baran.aydogan@uef.fi if you encounter any problems or have suggestions.
XACT leverages surface meshes as anatomical constraints together with extended options to the conventional ACT [Smith2012] [Yeh2017].
To create XACT surfaces from a Freesurfer folder, please use the prepXact command. The generated XACT file can then be used for fiber tracking using the track command with the --xact option.
The XACT file contains multiple surfaces that are used to apply anatomical constraints during tractography. These surfaces include the following 13 regions:
Label |
Description |
Abbreviation |
1 |
Left white matter |
L_WM |
2 |
Right white matter |
R_WM |
3 |
Left gray matter |
L_GM |
4 |
Right gray matter |
R_GM |
5 |
Left subcortical |
L_SUB |
6 |
Right subcortical |
R_SUB |
7 |
Cerebrospinal fluid |
CSF |
8 |
Cerebellar white matter |
CER_WM |
9 |
Cerebellar gray matter |
CER_GM |
10 |
Brain stem |
BS |
11 |
Inferior brain stem |
I_BS |
12 |
Abnormality |
ABN |
13 |
Background |
BG |
Important
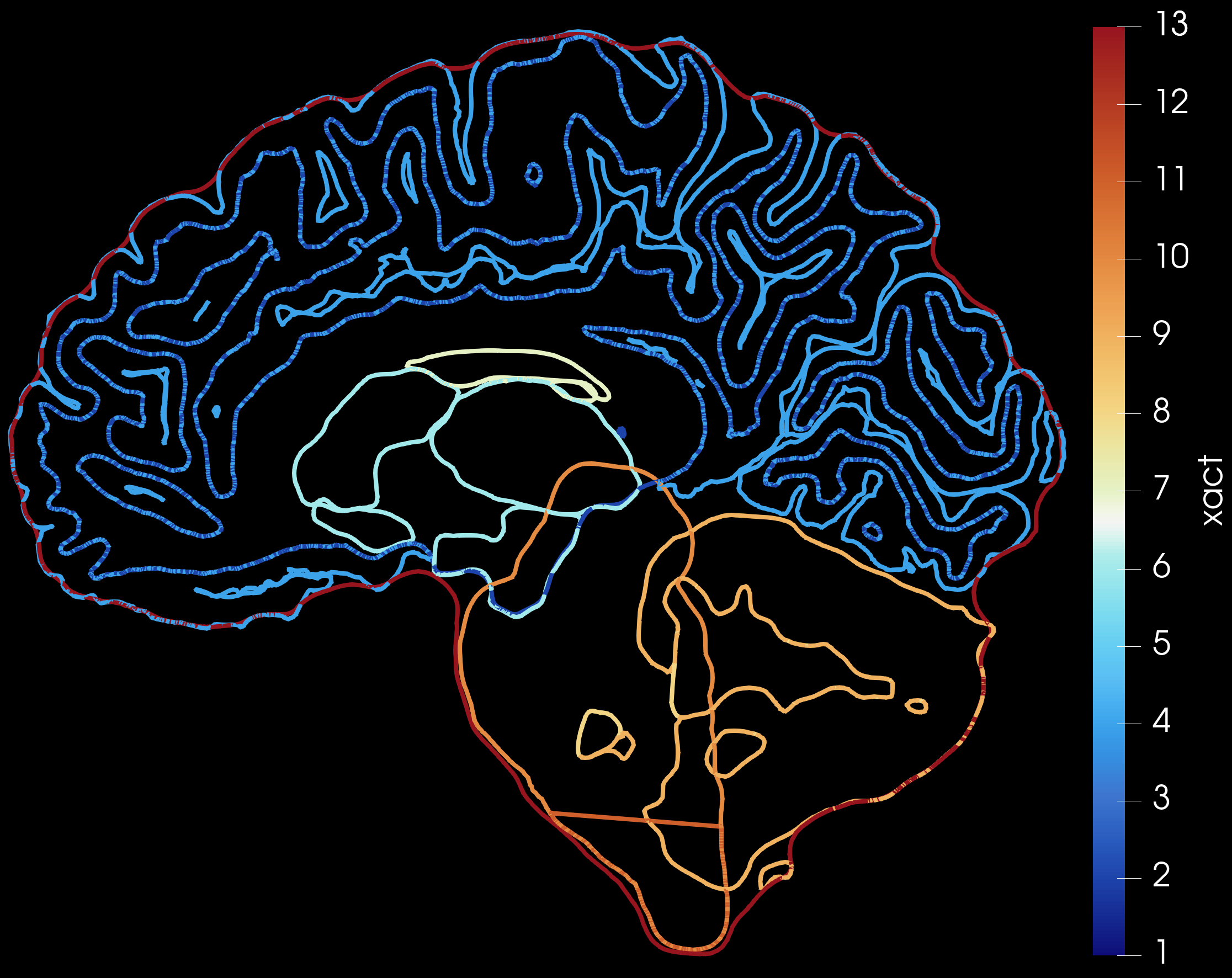
Known issue: The surfaces created by prepXact are known to intersect each other. This may cause problems for some applications.
While we are still working on improvements for future releases, we advise to check the surfaces carefully before use to ensure they are adequate for the application in question.
An example showing the intersecting surfaces is shown below:
Common rules
When the --xact option is used, the following rules are always applied:
Seeding: Seeds are randomly generated in white matter (L_WM, R_WM, CER_WM) and brain stem (BS).
Allowed endpoints: Streamlines are required to end inside gray matter (L_GM, R_GM, CER_GM), subcortical structures (L_SUB, R_SUB), brain stem (BS), abnormality (ABN), or background (BG).
Exclusion: Streamlines are discarded if they enter cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Default behavior
In addition to the common rules, Trekker applies specific rules for different regions by default. These rules control seeding within these regions and how streamlines behave upon entering or exiting them.
| Region | Seeding | Stop after entry | Stop before exit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex (L_GM, R_GM, CER_GM) | OFF | ON | OFF |
| Background (BG) | OFF | ON | OFF |
| Subcortex (L_SUB, R_SUB) | ON | OFF | OFF |
| Abnormality (ABN) | ON | OFF | OFF |
Note
Unless otherwise specified, --xact uses the default fiber tracking parameters in Trekker, e.g., minlength = 0, maxlength = infinite.
Modifying behavior
The default behavior can be modified using specific flags. These flags adjust the region-specific rules to accommodate different tracking requirements.
Flag |
Description |
Effect |
|---|---|---|
|
Performs tractography also within the intracortical regions defined in the XACT file (L_GM + R_GM + CER_GM). |
Enables seeding in cortex, disables stopping after entry, and enables stopping before exit. |
|
Performs tractography also within the cranial region defined in the XACT file (BG), which can be used for cranial nerve tracking. |
Enables seeding in background, disables stopping after entry, and enables stopping before exit. |
|
Streamlines are truncated before they exit subcortical regions (L_SUB + R_SUB), which is the convention in [Smith2012]. |
Enables stopping before exit for subcortical regions. |
|
Streamlines are truncated before they exit abnormality regions (ABN). |
Enables stopping before exit for abnormality regions. |
Important
--xact_intracorticaland--xact_cranialoptions only set anatomical constraints in order to obtain the streamlines confining to these regions. These options do not apply dedicated fiber tracking algorithms to obtain high-quality streamlines.For intracortical tractography, it is crucial to have high-quality diffusion data with sufficient spatial resolution and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Additionally, advanced modeling techniques such as multi-shell acquisitions and higher-order diffusion models may be necessary to accurately capture the complex fiber orientations within the cortex with tuned parameters used for fiber tracking.
For tractography outside of the brain (cranial), it is important to make sure that FODs are properly estimated in these regions. High-quality data and appropriate modeling techniques are essential for reliable results. Fiber tracking parameters may also need to be adjusted to account for the different diffusion characteristics in these areas.
Note
Inferior brain stem (I_BS) is a part of the brain stem (BS). While it is not used as a separate label during tractography, it is included for completeness and can be used for consequent filtering of streamlines.
Abnormality (ABN) region is optional. This region can be included to represent tumours or other lesions if they are present. Please use
prepXact’s--abnormalityoption to include this region in the XACT file. If not provided, the related rules are ignored.
References
